Latest E-Invoicing Rules and Turnover Limits (Updated 2025)
India’s e-invoicing system under GST continues to expand, bringing more businesses under its compliance umbrella. Whether you’re a trader, manufacturer, exporter, or small business owner, understanding the current turnover thresholds and new rules is crucial for avoiding penalties and ensuring seamless operations in 2025.
📢 What is E-Invoicing in GST?
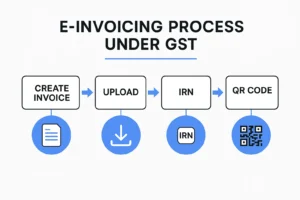
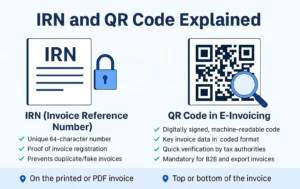
Under GST, certain businesses must generate invoices through the government’s Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). Each invoice is validated and assigned an Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and a QR code. This process makes the invoice legally valid and compliant.
📊 Turnover-Based E-Invoicing Mandates (As of 2025)
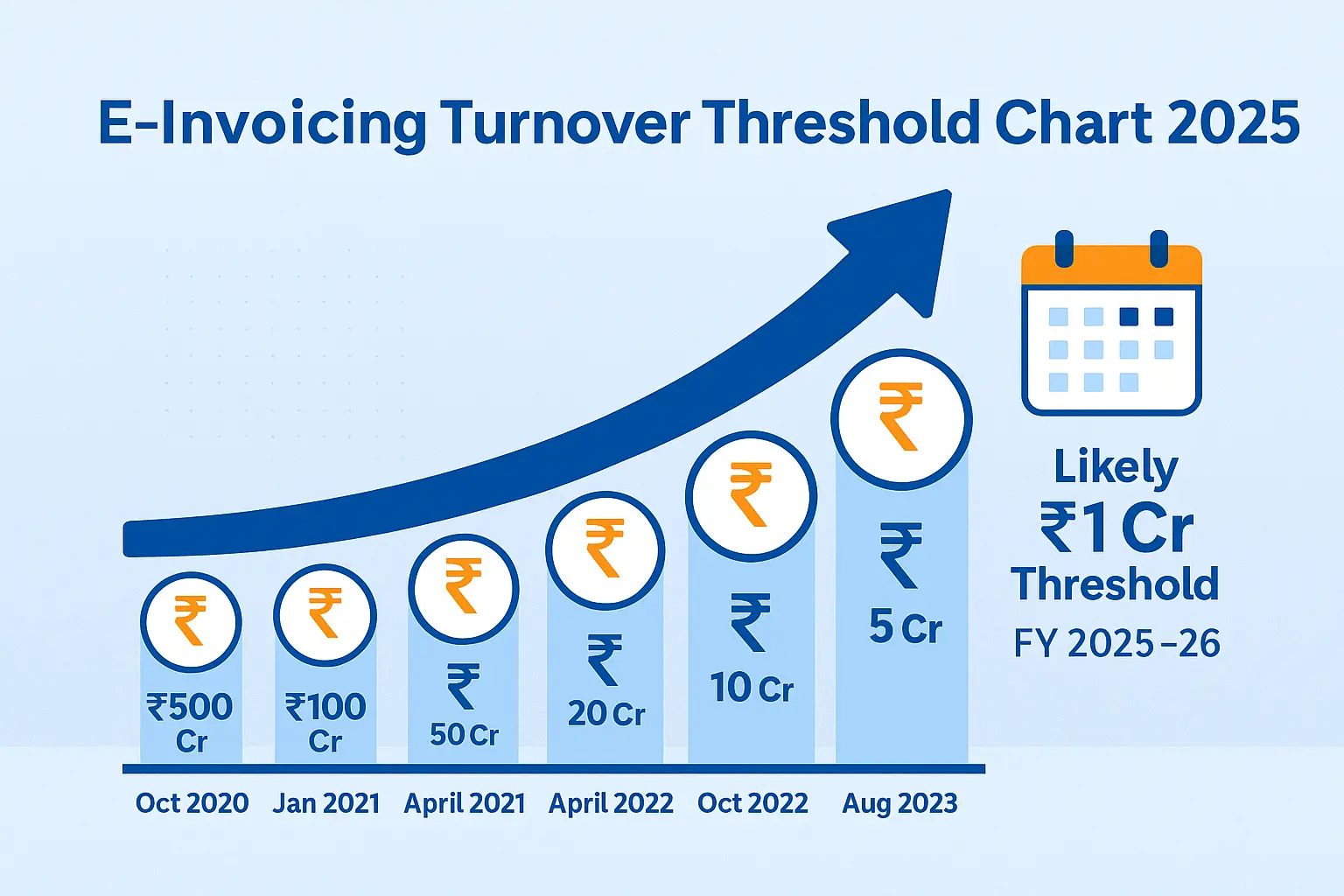
The following turnover limits apply for mandatory e-invoicing, based on aggregate turnover in any financial year since 2017–18:
- ✅ ₹500 crore and above – Mandatory from October 1, 2020
- ✅ ₹100 crore and above – From January 1, 2021
- ✅ ₹50 crore and above – From April 1, 2021
- ✅ ₹20 crore and above – From April 1, 2022
- ✅ ₹10 crore and above – From October 1, 2022
- ✅ ₹5 crore and above – From August 1, 2023
🚨 Upcoming Rule: Likely ₹1 Crore Threshold
The GST Council is expected to reduce the e-invoicing threshold further to ₹1 crore in turnover during FY 2025–26. This move will impact lakhs of micro and small enterprises that currently use regular invoices.
Pro Tip: If your turnover is above ₹1 crore, it’s wise to start preparing now to avoid last-minute compliance pressure.
🕒 New 30-Day IRN Reporting Rule (Effective April 1, 2025)
Businesses with turnover of ₹10+ crore or more are now required to report invoices to the IRP within 30 days of invoice generation. Failure to do so will render the invoice invalid.
🚫 This rule will soon apply to ₹5 crore+ turnover businesses, based on future notifications.
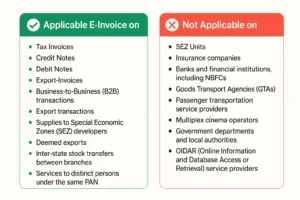
📂 Documents That Require E-Invoicing
- ➤ B2B Tax Invoices
- ➤ Export Invoices
- ➤ Credit Notes
- ➤ Debit Notes
📌 Key Benefits of E-Invoicing Compliance
- ✔ Auto-population of GSTR-1 and e-way bills
- ✔ Reduced chances of data mismatch
- ✔ Faster input tax credit (ITC) claim
- ✔ Stronger digital audit trail
🧾 Who is Exempt from E-Invoicing?
Entities exempt from e-invoicing include:
- ✖ Insurance companies
- ✖ Banks and NBFCs
- ✖ Goods Transport Agencies (GTAs)
- ✖ Passenger transport services
- ✖ SEZ units (SEZ developers are not exempt)
- ✖ Multiplex operators
- ✖ Government departments and local authorities
- ✖ OIDAR service providers
Conclusion
GST e-invoicing rules are evolving quickly. Staying updated with the latest turnover limits, reporting timelines, and exemptions ensures you avoid compliance risks. The sooner you adopt e-invoicing, the smoother your transition will be.
📌 Be Ready Before the ₹1 Crore Limit Hits
Millions of Indian businesses may soon be required to adopt e-invoicing. Don’t wait for the last-minute rush.
BizBharat E-Invoice is a secure, Excel-based solution that helps MSMEs generate unlimited e-invoices with IRN & QR code — 100% offline and API-free.
👉 Try BizBharat Now and stay ahead of compliance changes in 2025.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
₹5 crore and above. A new ₹1 crore threshold is expected soon.
From April 1, 2025, businesses with ₹10 Cr+ turnover must report invoices within 30 days of generation.
Yes. Aggregate turnover includes taxable, exempt, export, and inter-state supplies across all GSTINs under one PAN.
Yes. Voluntary compliance is allowed by registering on the IRP portal.